The gap between Washington and Oregon’s gas prices is almost exactly the amount of Washington’s CO2 tax, imposed by the Climate Commitment Act
Todd Myers
Washington Policy Center
According to AAA and GasBuddy, Washington state gas prices are about 25 cents per gallon more than Oregon. In December 2022, the prices were virtually identical. That gap is almost exactly the amount of Washington’s CO2 tax, imposed by the Climate Commitment Act (CCA).

This is not a surprise and matches the experience in California and elsewhere where CO2 taxes have been imposed. Despite that, tax supporters continue to claim it is having just a minor impact on prices.
One of the groups most active in claiming the impact of the CO2 tax is low is the Clean & Prosperous Institute. C&P is funded in part by BP and led by Reuven Carlyle, a former legislator who wrote the CCA and now runs a climate finance company.
Recently, C&P claimed, “Based on our running tracker of Washington gas prices relative to Oregon, Washington gasoline is less than 14 cents/gallon higher than the historical spread (as of June 24th): down 9 cents/gallon since the beginning of the year and roughly 10 cents/gallon since this time last year.”
The most recent CO2 price based on the auction of allowances of $29.92 per metric ton equates to 23.7 cents per gallon of gas and 29 cents per gallon of diesel. How does C&P claim the actual impact is less than half of the tax?
They achieve this by comparing current prices to a “historical spread” that begins in 2015.
C&P claims that “that carbon prices, unlike direct fuel taxes, tend to be less than fully passed through to the end-consumers.” To demonstrate this, they cite the Seattle Times saying, “From 2015 and 2022, a gallon of regular gasoline in Washington was on average 11 cents more than in Oregon.” Their argument is, “Washington gas prices used to be 11 cents higher than Oregon and now we are only 24 cents higher! See, the impact isn’t so much.”
That claim has some serious flaws.
Using the eight years from 2015-22 as a baseline ignores big changes in public policy that skew the comparison between Washington and Oregon.
Two easy ones come to mind.
Oregon’s low-carbon fuel standard took effect in 2017. The State of Oregon estimates the impact on gas prices in 2017 was just 0.32 cents per gallon. By 2022, their calculation shows the impact had increased to 6.92 cents per gallon. Using 2015-22 as a constant baseline ignores this significant change in prices. In 2023 the impact of Oregon’s LCFS jumped by nearly another three cents per gallon to 9.8 cents per gallon.
Additionally, Oregon increased its gas tax by two cents per gallon at the beginning of 2024. The price impact of Oregon’s LCFS in 2024 may be even higher since the rule became more restrictive at the beginning of the year.
Using a long-term baseline only works if all things are held basically equal. Between 2015 and 2024, Oregon taxes and regulations have – by their own calculation – increased gas prices by about 12 cents per gallon. Instead of reducing statistical noise, ignoring all of those changes increases the number of confounding factors. The effect of this is to make it look like the gap between Washington and Oregon’s prices are smaller than they really are. If all else had been held equal, Oregon’s gas prices would have gone from 11 cents per gallon less than Washington, to about a penny more.
The best, albeit imperfect, baseline is to use prices in the year before Washington’s CO2 tax took effect. There, the record is pretty clear. Average gas prices in the two states were almost identical, with Oregon prices slightly above Washington’s at a couple of points.
That all changed when 2023, with Washington’s prices jumping significantly above Oregon’s. Since that time, the gap between the two states has been close to the CO2 tax amount.
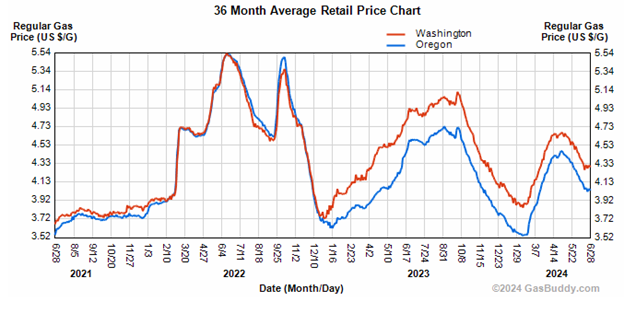
C&P claims looking at 2022 is invalid because, “Gasoline prices were hitting peaks (volatility and $/gallon that have yet to be topped) in 2022 due to global events.” Despite that volatility in total price, Oregon and Washington prices followed each other almost exactly. Amidst the chaos of world markets, the gap between the two states was stable. The fact that prices were virtually identical even in a time of volatility demonstrates that the comparison between the two states is robust. Their data proves the opposite of what they claim.
C&P’s argument amounts to “Although prices were virtually identical in the year leading up to the CO2 tax and the current gap in prices is almost exactly what the CO2 tax costs, we should ignore that because in 2016 Washington’s gas prices were higher than Oregon’s.”
I find it hard to believe they actually think this makes sense. For political and ideological reasons, some people want to believe the impact of the CO2 tax is small, so they give them the thin reed upon which to cling.
Earlier this year, C&P claimed that the relatively low CO2 tax prices this year were more normal and the high prices from last year were anomalous. It seems pretty clear that the prospect of the CO2 tax being repealed has depressed the market for CO2 allowances since they might become worthless in December.
But if C&P thinks I’m wrong, they can bet me. I bet $100 to charity that if the CCA isn’t repealed in November, prices at the CO2 allowance auction in December will jump above $50 per metric ton. If they actually believe what they are saying, they can take my money.
Ultimately, I expect the price gap to remain close to 24 cents per gallon for the rest of the year as auction prices for CO2 permits remain near the minimum. The fact that advocates of the CO2 tax have to play so many games to minimize the cost of their favored policy indicates they know the voters don’t think their climate policy is worth the cost.
Todd Myers is the vice president for research at the Washington Policy Center.
Also read:
- POLL: Why did voters reject all three tax proposals in the April 22 special election?Clark County voters rejected all three tax measures on the April 22 special election ballot, prompting questions about trust, affordability, and communication.
- Opinion: The war on parental rightsNancy Churchill argues that Olympia lawmakers are undermining voter-approved parental rights by rewriting key legislation and silencing dissent.
- Opinion: An Earth Day Lesson – Last year’s biggest environmental victories came from free marketsTodd Myers argues that Earth Day should highlight free-market solutions and grassroots innovation as more effective tools for environmental stewardship than top-down mandates.
- Opinion: Time to limit emergency clauses and give voters a choiceTodd Myers urges the governor to remove emergency clauses from bills that appear intended to block voter input rather than address real emergencies.
- Letter: C-TRAN Board improper meeting conductCamas resident Rick Vermeers criticizes the C-TRAN Board for misusing parliamentary procedure during a controversial vote on light rail.










